#bee species
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
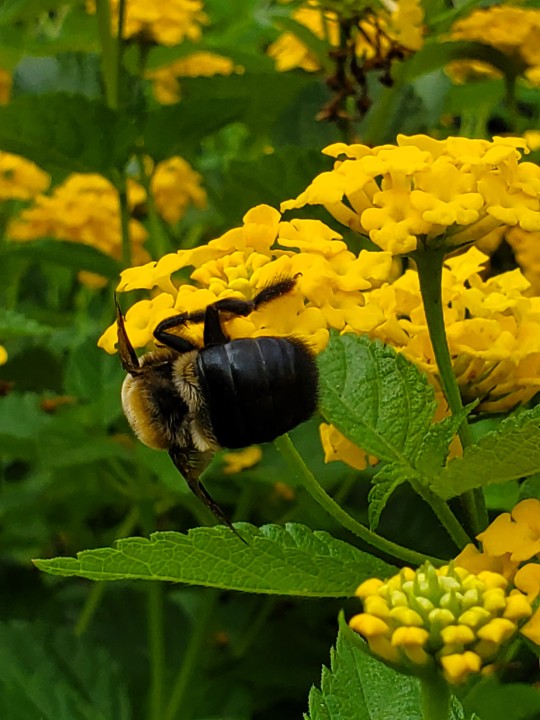
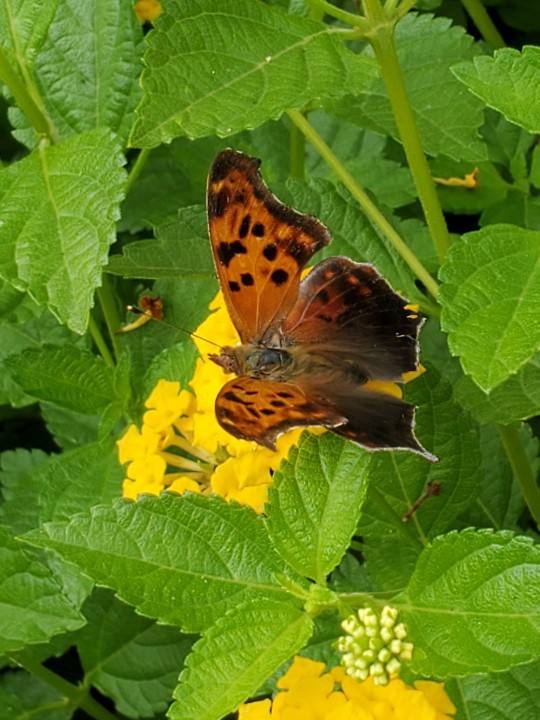
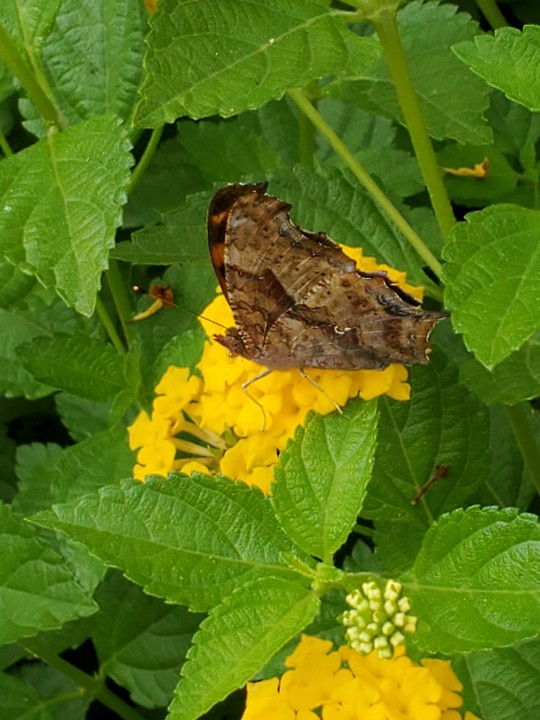
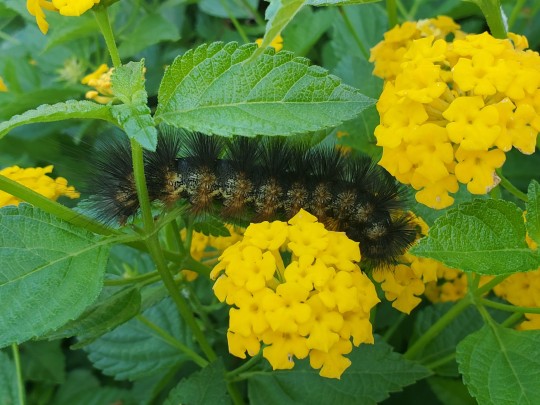
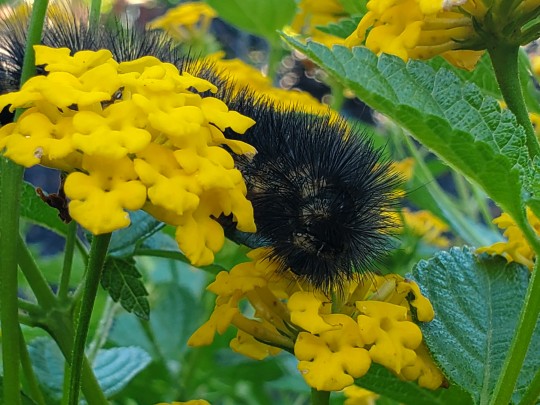









The lantanas by the fountain at school are a very popular hangout spot for all kinds of critters. Here we see:
an eastern carpenter bee 》 Xylocopa virginica (the big, plump boys that are so cute)
a question mark butterfly 》 Polygonia interrogationis (named for the silver mark on the underside of their hindwings)
and what I think is a tiger moth caterpillar of some variety 》 tribe Arctiini in the family Erebidae, subfamily Arctiinae (caterpillars are a bit tricky to identify sometimes).
Southeast Texas, 19 April 2024 (bee & butterfly), 23 April 2024 (caterpillar)
#not fungi#not a mushroom#amatuer mycology#mushrooms#mycology#fungi#mushroom hunting#mushrooms of texas#texas mushrooms#wild fungi#fungi of texas#fungarium#foraging texas#foraging#bugs#bug#bee#bees#butterfly#butterflies#caterpillar#bee species#butterfly species#caterpillar species#species identification#special interest#nature photography#goblincore#nature#butterfly feeding
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
"In 2021, scientists in Guelph, Ontario set out to accomplish something that had never been done before: open a lab specifically designed for raising bumble bees in captivity.
Now, three years later, the scientists at the Bumble Bee Conservation Lab are celebrating a huge milestone. Over the course of 2024, they successfully pulled off what was once deemed impossible and raised a generation of yellow-banded bumble bees.
The Bumble Bee Conservation Lab, which operates under the nonprofit Wildlife Preservation Canada, is the culmination of a decade-long mission to save the bee species, which is listed as endangered under the Xerces Society for Invertebrate Conservation...
Although the efforts have been in motion for over a decade, the lab itself is a recent development that has rapidly accelerated conservation efforts.
For bee scientists, the urgency was necessary.
“We could see the major declines happening rapidly in Canada’s native bumble bees and knew we had to act, not just talk about the problem, but do something practical and immediate,” Woolaver said.
Yellow-banded bumble bees, which live in southern Canada and across a huge swatch of the United States, were once a common species.

However, like many other bee species, their populations declined sharply in the mid-1990s from a litany of threats, including pathogens, pesticides, and dramatic habitat loss.
Since the turn of the century, scientists have plunged in to give bees a helping hand. But it was only in the last decade that Woolaver and his team “identified a major gap” in bumble bee conservation and set out to solve it.
“No one knew how to breed threatened species in captivity,” he explained. “This is critically important if assurance populations are needed to keep a species from going extinct and to assist with future reintroductions.”
To start their experiment, scientists hand-selected wild queen bees throughout Ontario and brought them to the temperature-controlled lab, where they were “treated like queens” and fed tiny balls of nectar and pollen.
Then, with the help of Ontario’s African Lion Safari theme park, the queens were brought out to small, outdoor enclosures and paired with other bees with the hope that mating would occur.
For some pairs, they had to play around with different environments to “set the mood,” swapping out spacious flight cages for cozier colony boxes.
And it worked.
“The two biggest success stories of 2024 were that we successfully bred our focal species, yellow-banded bumble bees, through their entire lifecycle for the first time,” Woolaver said.
“[And] the first successful overwintering of yellow-banded bumble bees last winter allowed us to establish our first lab generation, doubling our mating successes and significantly increasing the number of young queens for overwintering to wake early spring and start their own colonies for future generations and future reintroductions.”
Although the first-of-its-kind experiment required careful planning, consideration, resources, and a decade of research, Woolaver hopes that their efforts inspire others to help bees in backyards across North America.
“Be aware that our native bumble bees really are in serious decline,” Woolaver noted, “so when cottagers see bumble bees pollinating plants in their gardens, they really are seeing something special.”"
-via GoodGoodGood, December 9, 2024
#bees#insect#save the bees#xerces society#biodiversity#conservation#endangered species#wildlife conservation#canada#north america#climate action#climate news#good news#hope
6K notes
·
View notes
Text

Xerces Society: Announcing The State Of The Bees Initiative: Our Plan To Study Every Wild Bee Species In The U.S.
This is really exciting news! For those unaware, the Xerces Society has been focusing on invertebrate conservation for over fifty years, and has pioneered a lot of the work to bring awareness to the devastating losses of not only insects but other terrestrial and aquatic invertebrates. It gets its name from the Xerces blue butterfly (Glaucopsyche xerces), the first North American butterfly driven to extinction by human activities.
Even if you haven't heard of the Xerces Society, you've probably come across various "Save the Bees!" campaigns. These frequently focus on the domesticated European honey bee (Apis mellifera), which, while it may be important to crop pollination in many parts of the world, is not a part of natural ecosystems in places like the Americas and Australia, and can be considered an invasive species at times. With the rise of colony collapse disorder (CCD) particularly after the turn of the 21st century, where entire domestic honeybee colonies would die off, the need to preserve bees began to gain wider public acknowledgement.
But what many people don't realize is that it is the thousands upon thousands of other native bee species worldwide that are in greater danger of extinction. They don't have armies of beekeepers giving them safe places to live and treating them for diseases and parasites. More importantly, where honey bees may visit a wide variety of plants, native bees often have a much narrower series of species they visit, and they are quite vulnerable to habitat loss. Most bees are not as social as honey bees and live solitary lives, unseen by the casual observer.
Invertebrates in general often suffer from a lack of conservation information, meaning that particularly vulnerable species may fly under the radar and risk going extinct without anyone realizing until it's too late. This ambitious program by the Xerces Society aims to solve that problem, at least for the 3,600+ species of bee in the United States. If they can assign a conservation status to each one, then that strengthens the argument toward protecting their wild habitats and working to increase their numbers. Hopefully it will also prompt more attention to other under-studied species that are in danger of going extinct simply because we don't know enough about them.
#bees#save the bees#invertebrates#arthropods#insects#entomology#nature#wildlife#animals#ecology#environment#conservation#science#scicomm#endangered species#extinction#pollinators#Xerces Society#Xerces blue
598 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Oriental Blue Clearwing Moth: these moths were regarded as a "lost species" for more than 130 years, until they were finally sighted again in 2013
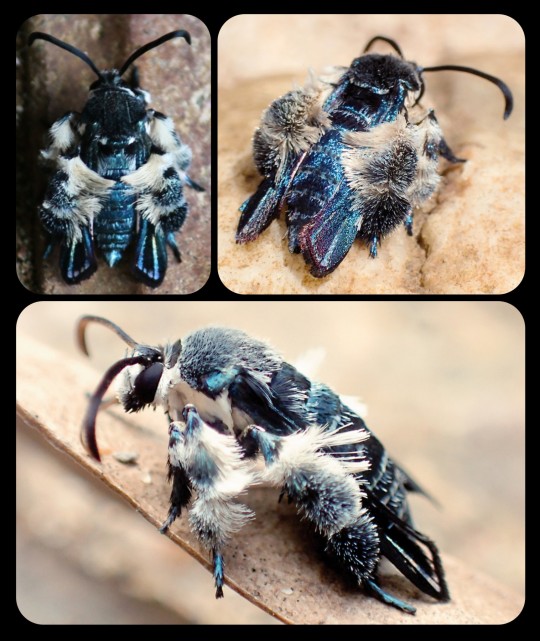

For more than 130 years, the Oriental blue clearwing moth (Heterosphecia tawonoides) was known only from a single, badly damaged specimen that was collected in Sumatra in 1887. There were no recorded sightings of this species again until 2013, when entomologist Dr. Marta Skowron Volponi unexpectedly found the moths feeding on salt deposits that had accumulated along the riverbanks in Malaysia's lowland rainforest.
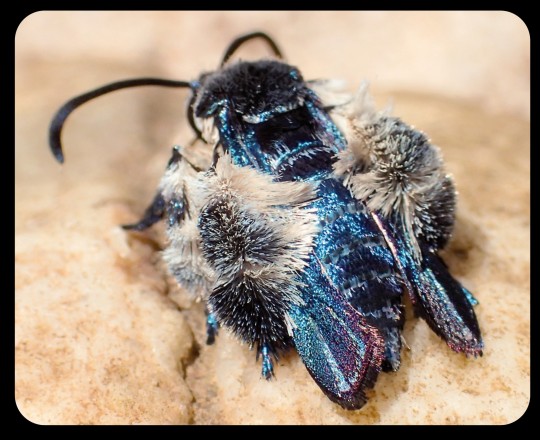

These moths were observed by researchers again in 2016 and 2017, and research indicates that the moths are actually bee-mimics, as they mimic the appearance, sound, behavior, and flight patterns of local bees. Their fuzzy, bright blue appearance might seem a little out of place for a bee-mimic, but those features do appear in several different bee species throughout Southeast Asia.
When the moths are in flight, they bear a particularly strong resemblance to the bees of the genus Thyreus (i.e. cuckoo bees, otherwise known as cloak-and-dagger bees), several of which are also bright blue, with banded markings, dark blue wings, fuzzy legs, and smooth, rounded antennae. The physical resemblance is compounded by the acoustic and behavioral mimicry that occurs when the moths are in flight.
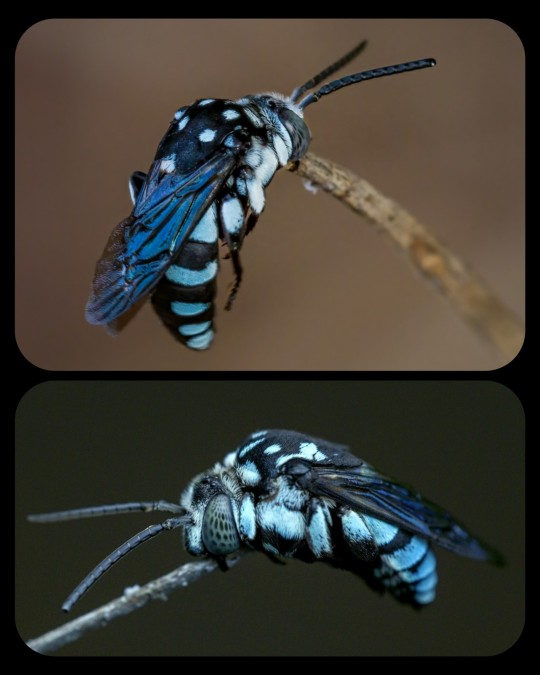

Cloak-and-Dagger Bees: the image at the top shows an Indo-Malayan cloak-and-dagger bee (Thyreus novaehollandiae) in a sleeping position, holding itself upright with its mandibles clamped onto a twig, while the image at the bottom shows a Himalayan cloak-and-dagger bee (T. himalayensis) resting in the same position
The moths also engage in "mud-puddling" among the various bees that congregate along the riverbanks; mud-puddling is the process whereby an insect (usually a bee or a butterfly) draws nutrients from the fluids found in puddles, wet sand, decaying plant matter, carrion, animal waste, sweat, tears, and/or blood. According to researchers, the Oriental blue clearwing moth was the only lepidopteran that was seen mud-puddling among the local bees.
Dr. Skowron Volponi commented on the unusual appearance and behavior of these moths:
You think about moths and you envision a grey, hairy insect that is attracted to light. But this species is dramatically different—it is beautiful, shiny blue in sunlight and it comes out during the day; and it is a master of disguise, mimicking bees on multiple levels and even hanging out with them. The Oriental blue clearwing is just two centimeters in size, but there are so many fascinating things about them and so much more we hope to learn.
This species is still incredibly vulnerable, as it faces threats like deforestation, pollution, and climate change. The president of Global Wildlife Conservation, which is an organization that seeks to rediscover "lost species," added:
After learning about this incredible rediscovery, we hope that tourists visiting Taman Negara National Park and picnicking on the riverbanks—the home of these beautiful clearwing moths—will remember to tread lightly and to take their trash out of the park with them. We also recommend that Americans learn about palm oil production, which is one of the primary causes of deforestation in Malaysia.
Sources & More Info:
Phys.org: Bee-Mimicking Clearwing Moth Buzzes Back to Life After 130 Years
Mongabay News: Moth Rediscovered in Malaysia Mimics Appearance and Behavior of Bees to Escape Predators
Journal of Tropical Conservation Science: Lost Species of Bee-Mimicking Clearwing Moth, H. tawonoides, Rediscovered in Peninsular Malaysia's Primary Rainforest
Frontiers in Zoology: Southeast Asian Clearwing Moths Buzz like their Model Bees
Royal Society Publishing: Moving like a Model - mimicry of hymenopteran flight trajectories by clearwing moths of Southeast Asian rainforests
Medium: Rediscovery in a Glint of Blue
re:wild.org: The "Search for Lost Species" Project
#lepidoptera#moths#heterosphecia tawonoides#oriental blue clearwing moth#entomology#insects#cute bugs#nature#animals#lost species#mimicry#evolution#bees#southeast asia#Malaysia#colorful moths#bee mimic#science
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Therapy Humans
After being in a war for millions of years transformers gotta be really fucked up. So I imagine with humans being nice and soft and having therapists that we'll be therapy dog humans.
#transformers#humans are cats#humans are space cats#transformers x human#not really but eh#bumblebee would love sam holding his face on his lap#Optimus has tranquil conversations over tea/energon with cade#mirage seems like the type of bot to love physical contact to relax#so platonic cuddling!#or not 😏#mirage x noah#barn husbands#idk sam ships name with bee#sams and bee are like the same age right? well in their species#im no longer some 15 year old who uses questionable stuff to cope because I didn't know any better#i got standards#I'm assuming he's like 17#once again i don't know a lot about of tf outside of fics#and bee is like 16-18
624 notes
·
View notes
Note
GASP bloo bee is sooo preeettyyy, may I touch the face/fuzzy fur?~


Bee my guests~
#digital sketch#digital art#original character#original species#bugs#insects#bug oc#monster oc#buff girls#monster girlfriend#carpenter bee#robber fly#terato#asks#art stuff#oc: bloo bee#oc: flygirl
679 notes
·
View notes
Text




black bees
2024/06/08
#photography#photographers on tumblr#nature#naturecore#nature photography#aesthetic#flowers#adventure#flora#poland#garden#botanical garden#botanic#black bee#bee#protected#protected species#insect
290 notes
·
View notes
Text

"I love what you did with your hair"
artfight revenge for @hissydyke with @arthroart as collateral damage. thought it'd be fun to draw both of the colorful bee ladies on my 2024 hit-list together.
#bflyart#watercolors#artfight#bug people#bees#hymenoptera#apidae#megachilidae#Xylocopa caerulea#Mellissodes communis#Megachile rotundata#(she's a hybrid species)#idk the pink one's orientation and its none of my business but the word 'buzzbians' bubbled up in my brain several times while drawing this
305 notes
·
View notes
Text





I made a Bee AU bc I can
I love bugs SO MUCH y'all
#dick grayson#jason todd#tim drake#damian wayne#stephanie brown#cassandra cain#f: dc#dc#scribbles#designs#bee dcau#yes ik a lot of these are hiveless bee species but idc#50#100#500
595 notes
·
View notes
Text
"The world’s largest hornet, an invasive breed dubbed the “murder hornet” for its dangerous sting and ability to slaughter a honey bee hive in a matter of hours, has been declared eradicated in the U.S., five years after being spotted for the first time in Washington state near the Canadian border.
The Washington and U.S. Departments of Agriculture announced the eradication Wednesday [December 18, 2024], saying there had been no detections of the northern giant hornet in Washington since 2021...
“I’ve gotta tell you, as an entomologist — I’ve been doing this for over 25 years now, and it is a rare day when the humans actually get to win one against the insects,” Sven Spichiger, pest program manager of the Washington State Department of Agriculture, told a virtual news conference.
The hornets, which can be 2 inches (5 cm) long and were formerly called Asian giant hornets, gained attention in 2013, when they killed 42 people in China and seriously injured 1,675. In the U.S., around 72 people a year die from bee and hornet stings each year, according to data from the National Institutes of Health.
The hornets were first detected in North America in British Columbia, Canada, in August 2019 and confirmed in Washington state in December 2019, when a Whatcom County resident reported a specimen. A beekeeper also reported hives being attacked and turned over specimens in the summer of 2020. The hornets could have traveled to North America in plant pots or shipping containers, experts said.
DNA evidence suggested the populations found in British Columbia and Washington were not related and appeared to originate from different countries. There also have been no confirmed reports in British Columbia since 2021, and the nonprofit Invasive Species Centre in Canada has said the hornet is also considered eradicated there.
Northern giant hornets pose significant threats to pollinators and native insects. They can wipe out a honey bee hive in as little as 90 minutes, decapitating the bees and then defending the hive as their own, taking the brood to feed their own young.
The hornet can sting through most beekeeper suits, deliver nearly seven times the amount of venom as a honey bee, and sting multiple times. At one point the Washington agriculture department ordered special reinforced suits from China.
Washington is the only state that has had confirmed reports of northern giant hornets. Trappers found four nests in 2020 and 2021.
Spichiger said Washington will remain on the lookout, despite reporting the eradication. He noted that entomologists will continue to monitor traps in Kitsap County, where a resident reported an unconfirmed sighting in October but where trapping efforts and public outreach have come up empty...
“We will continue to be vigilant,” Spichiger said."
-via AP News, December 18, 2024
#murder hornets#insects#entomology#invasive species#endangered species#bees#save the bees#hornets#united states#north america#washington state#british columbia#canada#good news#hope
737 notes
·
View notes
Note
if you ever want to dip your toes into the more creepy side, in the episode "a health of information" a disease called swamp fever apparently turns living ponies into trees!! it always freaked me out, and since it was in the later seasons, it just wasn't developed upon (of course :P) there's a screenshot of one of the doctor ponies holding up a book that shows the cycle of transformation-- the stage where they've still got limb-like roots is so so creepy!!

HEY WHAT???? HEY WHAT. WHAT THE HECK IS THIS
#ask#a health of information#oohhogh the bees are immune to a disease that affects ponies!#YEAH THATS HOW DISEASES WORK#VERY FEW ARE ACTUALLY TRANSMISSABLE BETWEEN SPECIES#MUCH LESS BETWEEN PHYLUMS!!?!?!?!??!?!??!#ssg swamp fever
194 notes
·
View notes
Text

So uh- can someone bring me back to reality? Because I know we can all agree Grunkle Stanley is the more attractive twin but like.. I’m explicitly attracted to this realistic head of him.
Not him in Scary-oke episode.
This head.
His decapitated head is so fine.
#hear me out#please#gravity falls#stanley pines#I think it’s the asexual in me#or maybe the way he’s looking at me??#you think he keeps bees?#like-#illegal bees of course#probably imported from some foreign country#and an invasive species#but he keeps bees#someone slap me#please please please#i’m begging
49 notes
·
View notes
Photo
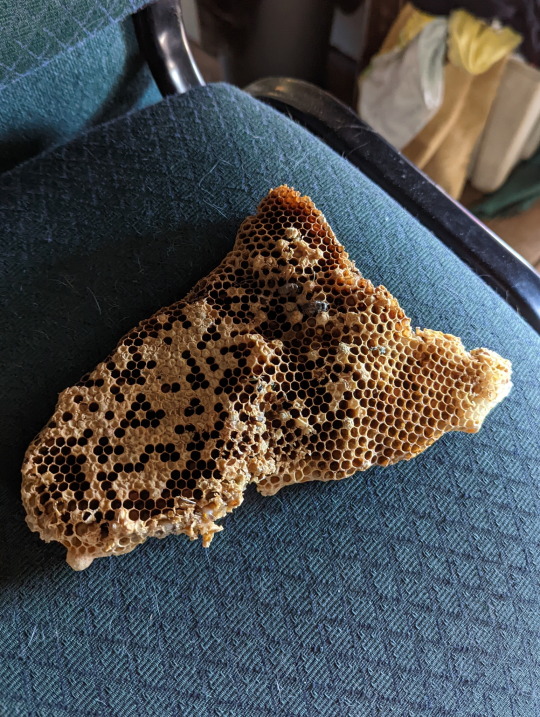
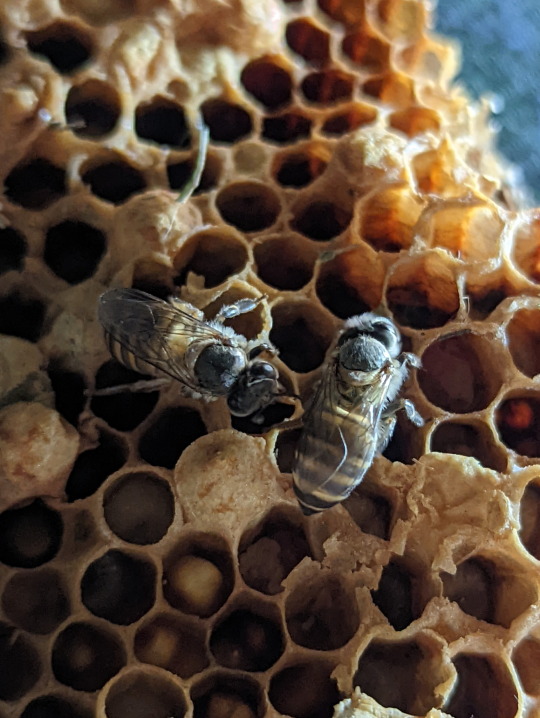
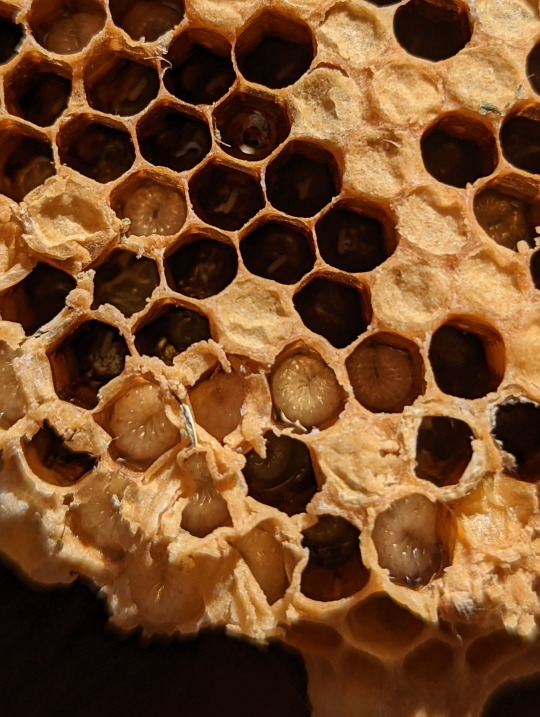
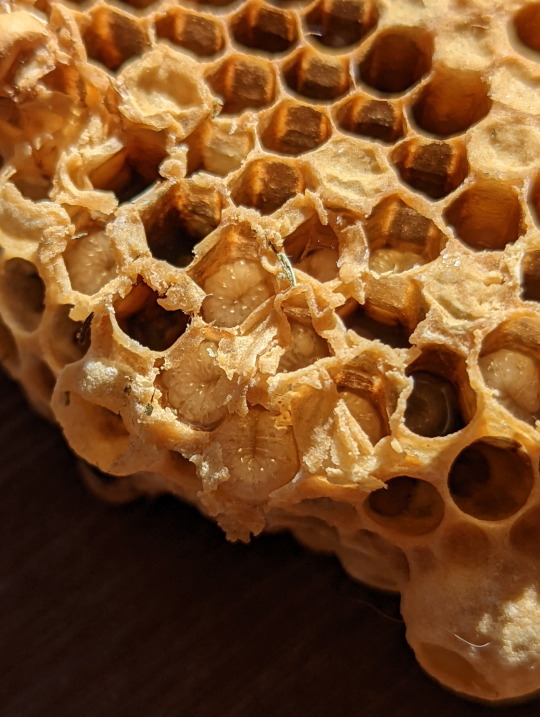
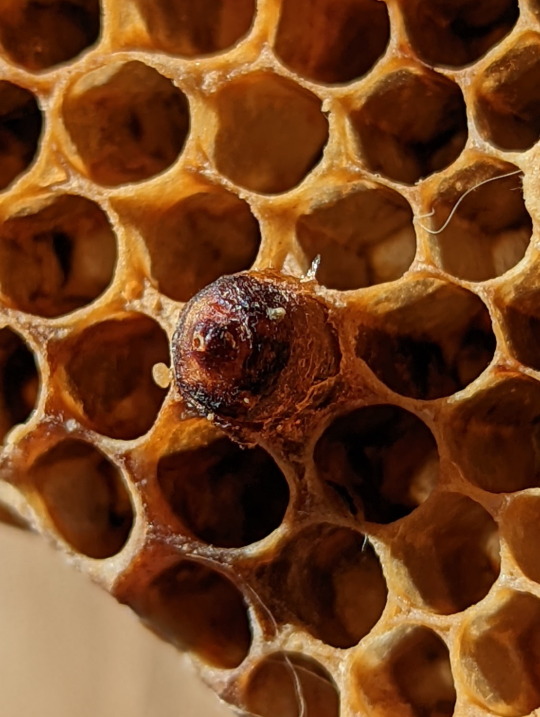
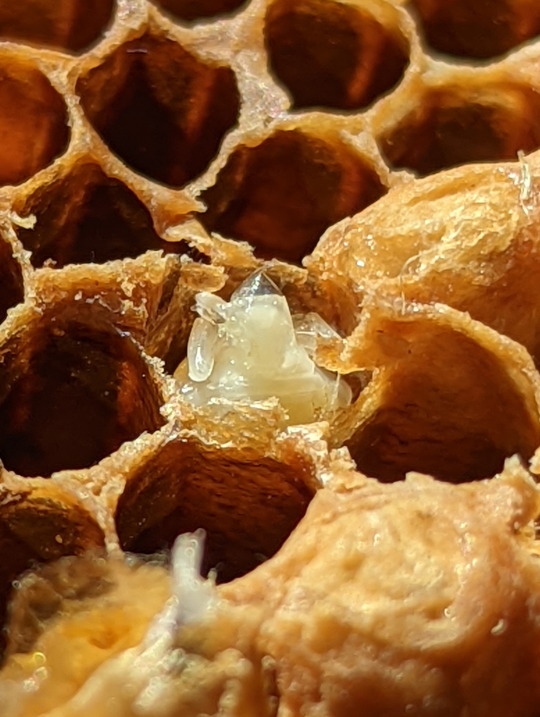
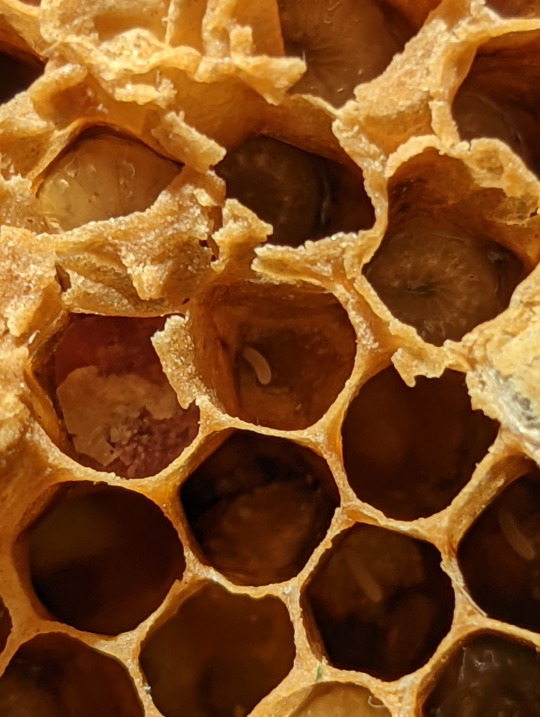
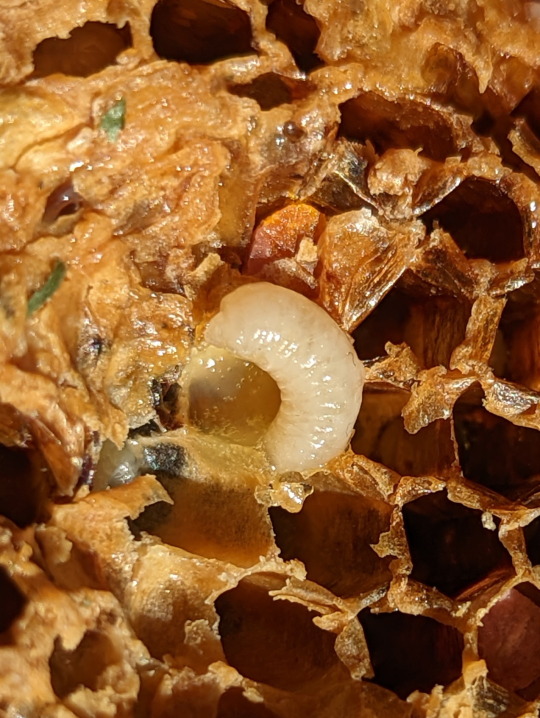




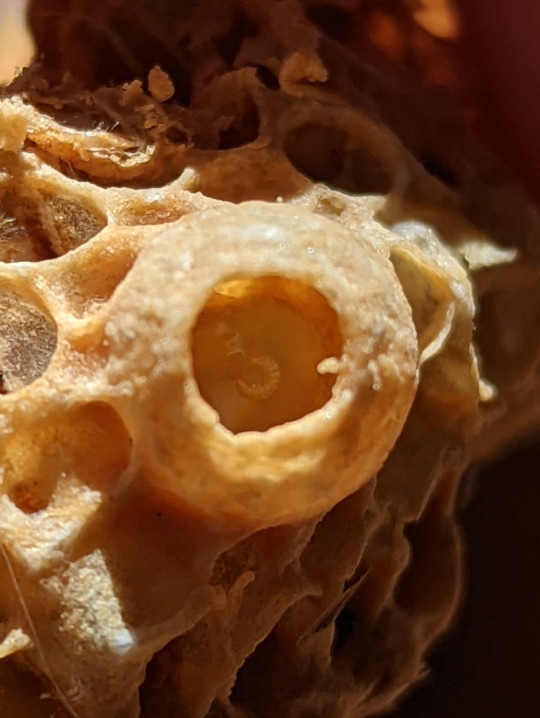
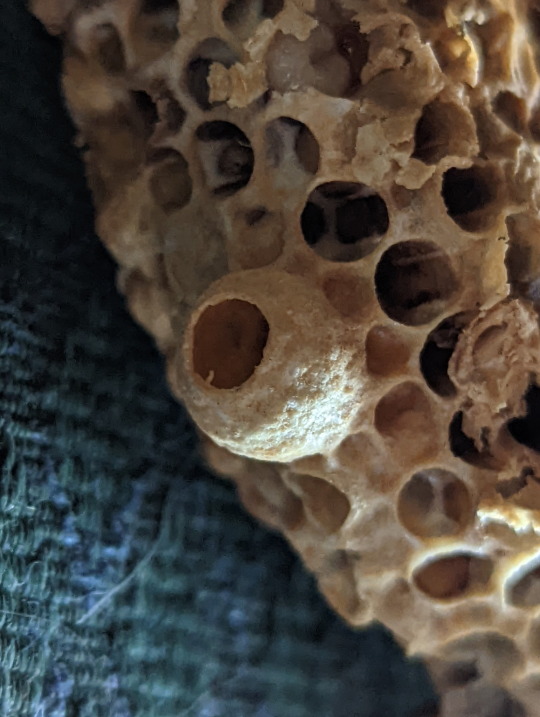




Nest of the Asian Honeybee
Here we have the poisoned nest of the Asian Honeybee (Apis cerana). If you’re wondering why the nest was poisoned, it’s because this species is actually quite damaging to this area. The Asian Honeybee not only leaves in competition with native bees over nesting areas and food, but they may also carry a certain nasty mite known as the ‘Varroa mite’ (genus Varroa), which can be detrimental to European Honeybee populations (Apis mellifera) (1).
Lets take a closer look at this nest shall we. First we’ll start off with the eggs. You can see an egg inside a brood cell in picture 9. The eggs are very small, and take about three days to develop. After which the fat little larvae emerge, curling up and waiting to be fed by the worker bees. When the larva becomes large enough, the brood cell will be sealed, so the larva’s pupation will be undisturbed. The adult bee will chew its way out of the cell after emerging from the pupae (2).
You can tell which brood cell belongs to which kind of bee based on its appearance. The drones have a distinctly dome-shaped cap with a large pour in the center (pic. 7). Then, of course, there’s the queen’s brood cell, which is large, round and on the edge of the nest (pics 5-6) (3).
When it comes to this species, it’s important to stay informed about the ways in which they are damaging for the environment.
Source (1)
Source (2)
Source (3)
Apis cerana
14/07/22
#Apis cerana#Asian Honey Bee#Apis#Cavity-nesting Honey Bees#Honey Bees#Apini#Anthophila#Bees#Hymenoptera#Varroa#Varroa Mites#Acari#Mites#invasive species#bugs#bugblr#bugs tw#bug#insects#insecta#insectblr#insects tw#entomology#insect#Arthropods#Arthropoda#beehive#hives#nests#invertblr
597 notes
·
View notes
Text

black bee
2024/06/08
#photography#photographers on tumblr#nature#naturecore#nature photography#aesthetic#flowers#adventure#flora#poland#garden#botanical garden#botanic#bee#black bee#insect#protected species
132 notes
·
View notes
Text

Georgia Mason Bee (Osmia georgica)
June 24, 2023
Southeastern Pennsylvania
I knew that this was a new bee for me when I shot it, but it only just got IDed on iNaturalist, 7 1/2 months later. I used to research my own IDs, but I've gotten a bit lazy about that since I discovered iNat, and also I realized how often I used to be plain wrong.
#63rd species in Pennsylvania for me#bee#bees#photographers on tumblr#bug#bugs#Osmia georgica#mason bees#georgia mason bee#bugblr#entomology#insects#insect#nature#animals#wildlife photography
118 notes
·
View notes
Text

Here's shoto!! If I had to pick a fav from mha, it's definitely Shoto Todoroki :) (My pen weight isn't calibrated right, so my lines have been pretty shaky, but I think it came out okay?)
#art#digital art#my art#mlp fim#mha#mha fanart#mha shoto#shoto todoroki#here's another bee fact!#did you know There are more than 4000 species of native bees in the US alone?
21 notes
·
View notes